NEOSCAN Micro CT technology combines X-ray imaging and computerized reconstruction to provide high-resolution 3D imaging and analysis of objects in a non-destructive manner.
High-resolution, non-destructive acquisition of the following information about the sample:

NEOSCAN Micro CT can obtain structural information (cavities and pores) and density information (compositional differences) without destroying the sample.
At the same time, a 3D model can be output for simulation and analysis, which has a wide range of applications in many industries:
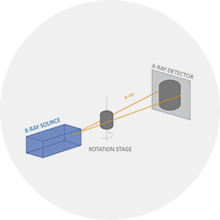
During the scanning process, the sample stage is rotated in fixed steps and angles. After each rotation, the X-ray beam passes through the sample and the detector records the corresponding projection data. With multiple rotation angles and projection data collection, information about the projection of the sample in different directions can be obtained.
The collected projection data is used to reconstruct the image using a computerized reconstruction algorithm. The most commonly used algorithm is Filtered Back Projection, which reconstructs a 3D image of the sample by filtering and back-projecting the projection data.

The reconstructed 3D image can be subsequently processed through image processing and analysis, including denoising, enhancement, segmentation, 3D visualization and other operations, in order to better observe and analyze the internal structure and characteristics of the sample.
If you want to know more about the product information, book a sample or consult the after-sales service, you are welcome to call our hotline 400 857 8882 or leave us a message online, we receive your message will be the first time to reply to you.